24.07.2025 / 08:30
Navigating Market Data License Management
License Management

Capture the true value of market data and vendor-product solutions by exploring the “Seven Cs”.
Market data products and services are expensive. To get more value out of market data, it is helpful to understand the following:
- There are market data product and service features
- There are levers in place to steer them
- and, conveniently, all of these features and levers start with the letter C
Product and service features define how they contribute to the output of the end-user. Here are the market data product & service features:
Content is king in market data and financial information services. Content makes the markets move. The more important the content, the higher the value – and the costs. Content sourcing and evaluation strategies include:
- Assessing relevance: Constantly evaluate the pertinence of content. What was crucial yesterday might not hold the same value today.
- Source reliability: Verify the credibility of information sources. Reliable, well-established sources are fundamental for accurate decision-making.
- Cost-benefit analysis: Weigh the costs against the potential insights and advantages gained from the content. High costs can be justified by high returns on information.
Connectivity is all about providing the connections between market participants as offered by the vendors. It ensures that content reaches the intended recipient, with appropriate speed and security. When considering connectivity in decision making, be sure to take the following into account:
- The nature of data access: Efficient connectivity ensures targeted and commensurate access to market data – whether real-time, snapshot, or delayed – enabling timely and informed decision making.
- Integrating diverse data sources: A well-connected market data system can integrate data from various sources, providing a comprehensive market view. This integration is key for complex analyses and strategies that require diverse data inputs.
- Global reach: Modern connectivity transcends geographical boundaries, allowing global market participation and access to international data.
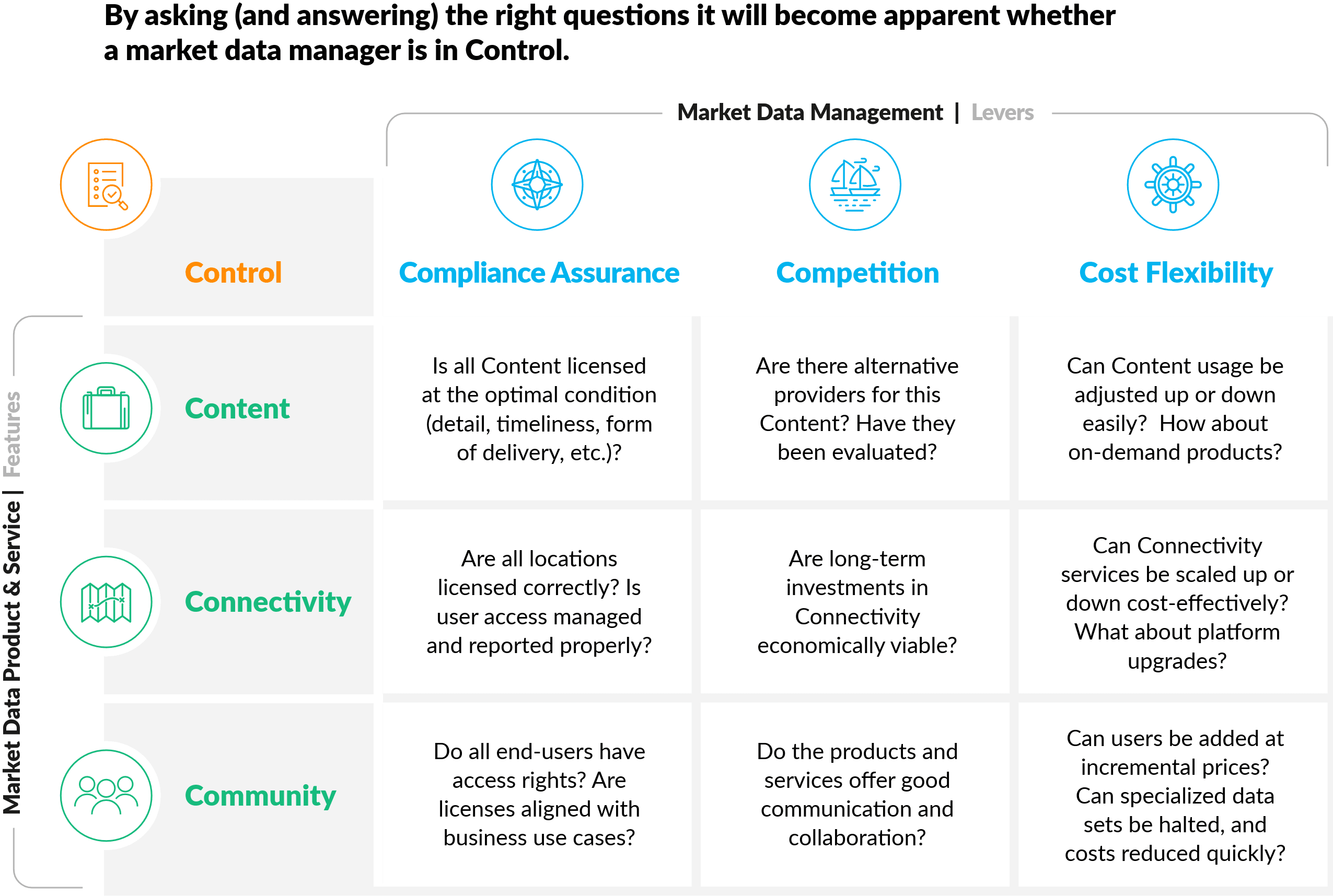
By applying the levers to the features, a number of relevant questions can be defined. Once they have been answered, the level of control (or market data spend) becomes clearer.
Community refers to the market participants in their actual roles, such as trading counterparties, researchers, or recipients of credit ratings. Members of a community communicate, collaborate (for example, through chat), and can discuss the elements of a potential trade. Further, they ask questions about a piece of research, or provide financial information. In terms of market data value added, the crucial community features of a of vendor’s products solutions can be characterized by:
- Collective intelligence: The community is a source of collective intelligence, offering diverse viewpoints, analysis, and insights. Does the vendor offer this access?
- Networking and opportunities: Networking within the community opens doors to new business opportunities, partnerships, and potential clients.
- Influence on market sentiment: This occurs through discussions and shared opinions, as showcased by “talking heads” for vendor products.
As an overlay, there is a number of product and service levers that determine how much influence a market data manager has over market data spend. Here are the market data management LEVERS:
Compliance assurance is what a product or service does, or offers, to make a bank, asset manager, or otherwise, compliant with rules and regulations. This includes the terms and conditions of agreements with the wide range of contracted vendors. Be sure to keep in mind:
- The relevance of vendor contracts and regulations: Robust compliance assurance minimizes the risk of vendor-, exchange-, or regulator imposed fines. Optimal compliance strikes the right balance cost-wise.
- Compliance evaluation strategies: Market data managers must thoroughly investigate a vendor’s compliance requirements (such as terms and conditions for data access), data quality controls, data lineage, data architecture, and security measures.
Competition within a certain space tells us whether market data product or service offerings are interchangeable with other products or services, or whether they are so unique that you cannot operate without them.
The competition lever examines the competitive landscape for a particular market data product or service. Is it a unique offering, or are there readily available substitutes?
Limited competition often translates to higher prices and less negotiating power for the buyer. Within the market data landscape, a number of near-monopoly providers can command high prices, since they are aware of the value that their content provides for end-user firms. An important competition evaluation strategy for market data managers involves conducting thorough market research by identifying alternative providers and assessing their strengths and weaknesses.
Cost flexibility relates to the level of ease with which adjustments within the product and service offerings can be made. How easily can a switch from modul A to module B be made, even when the total costs (and revenue for the selling vendor) decrease? Can it be scaled up or down easily? Are there modular options?
High-cost flexibility allows to optimize spending based on evolving needs. It also avoids a lock-in into long-term contracts for services no longer required.
Whenever possible, market data managers should prioritize vendors who offer flexible contracts, modular pricing, and usage-based billing.
In summary, features indicate the value and contributions of what market data vendors offer to an organization. Levers are about what a market data manager, can do to steer and influence them, to find what works best for an institution. Combined, they tell whether you are in Control – the seventh C!





